North Star Metric: A Guide for Product Managers
Understand how it helps product teams guiding towards success and keeping it aligned.
👋🏻 Hey there, welcome to the #27th edition of the Product Space Newsletter, where we help you become better at product management.
Product metrics are the backbone of a product manager's decision-making process and North Star Metric is one of the most important of them. In this article, we’ll dive deeper to explore what this metric entails for product management.
What is the North Star Metric in Product?
In product management, the concept of the North Star Metric (NSM) serves as a guiding light, much like the actual North Star has historically helped navigators find their way. It represents a single, critical metric that captures the core value your product delivers to customers.
This metric is not just another KPI (Key Performance Indicator); it’s the one metric that your entire product team should rally around to ensure consistent growth and long-term success.
Why is the North Star Metric Important?
If each crew member in a ship start rowing in a different direction, what would it look like? That's what product development can feel like without a clear, unifying metric. Here's why your NSM is crucial:
Alignment: It unites cross-functional teams under a shared objective, ensuring everyone from engineering to marketing is rowing in the same direction.
Focus on Value: By emphasizing the metric that best represents user value, you naturally prioritize initiatives that matter most to your customers.
Simplified Decision Making: When faced with tough choices, teams can ask, "How does this impact our North Star Metric?" This clarity can cut through analysis paralysis.
Balanced Growth: A well-chosen NSM encourages sustainable growth by balancing user value with business outcomes.
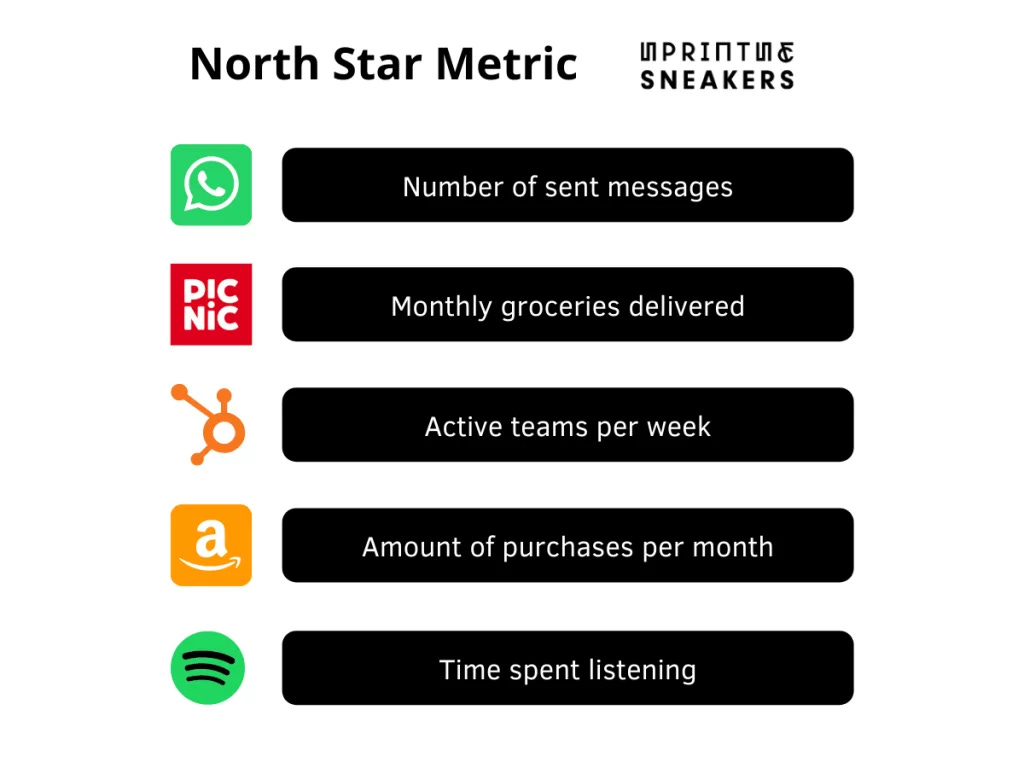
For example, a company like Spotify may use “Time spent listening” as their North Star Metric. This metric directly correlates with customer engagement and satisfaction, which ultimately impacts subscription renewals and ad revenue. By focusing on increasing the time users spend listening to music, Spotify can ensure that their team’s efforts are aligned with what truly matters for their business.
Key Components of the North Star Framework
The North Star Framework isn't just about picking a metric; it's a holistic approach to product strategy. Here are its key components:
Customer Value: Your NSM should reflect the value your product provides to customers. It should be something that, when improved, clearly indicates that your customers are deriving more value from your product.
Business Impact: While focusing on customer value is crucial, your NSM should also align with your company’s business goals. It’s about finding that sweet spot where customer satisfaction drives business success.
Measurability: Your NSM must be quantifiable. If it can’t be measured, it can’t be improved. Ensure that the metric you choose is something that can be tracked and reported on regularly.
Implementing the North Star Product Framework
Now that we understand the components, let's walk through the process of implementing the North Star Framework:
Identify your product’s core value: Start by understanding the core value your product provides to customers. This will help you brainstorm potential metrics that reflect this value. What's the primary benefit users get from your product? For a social media platform, it might be connection; for a productivity tool, it might be time saved.
Brainstorm potential metrics: List out metrics that could represent this core value. Don't self-censor at this stage.
Evaluate and select the best metric: Choose the metric that best aligns with long-term user value and business success. It should be:
A leading indicator of success
Specific
Actionable
Measurable
Communicate and align teams: Share the framework across your organization, explaining its importance and how each team contributes.
Embed it in your workflow: Once chosen, the NSM should become a central part of your team’s workflow. It should guide decision-making, be a key topic in team meetings, and be visible on dashboards and reports.
Monitor and iterate: Regularly review your NSM to ensure it remains relevant as your product and market evolve. Be prepared to iterate on it as needed.
Examples of North Star Metrics
Understanding the NSM becomes clearer with concrete examples. Let’s look at some well-known companies and their North Star Metrics:
Facebook: “Daily Active Users” is a key NSM for Facebook. It reflects the platform’s engagement level and is directly tied to ad revenue.
Airbnb: “Nights Booked” is a metric that captures the core value Airbnb provides—connecting travelers with unique accommodations, which is essential for revenue generation.
Slack: “Messages sent” within a team is
Why it works: Represents active communication and collaboration
Inputs: User onboarding, integration with other tools, notification settings
Results: Team productivity, customer retention, workspace growth
Amazon: Number of purchases per month
Why it works: Indicates customer satisfaction and platform stickiness
Inputs: Product selection, pricing, delivery speed, user reviews
Results: Revenue growth, market share increase
Example of a Bad North Star Metric
Not every metric is a good NSM. An example of a poorly chosen NSM might be “Number of Downloads” for a mobile app. While it’s tempting to focus on this metric, as it seems to indicate growth, it doesn’t necessarily reflect the core value provided to users.
A high number of downloads may not lead to sustained engagement or revenue, especially if users download the app but don’t actively use it. This misalignment can lead teams to prioritize short-term acquisition strategies over long-term engagement and retention, ultimately harming the product’s success.
Challenges in Applying the North Star Framework
Applying the North Star Framework is not without its challenges:
Choosing Vanity Metrics: Be wary of metrics that look good but don't correlate with real value or sustainable growth.
Neglecting User Value: Don't let short-term business goals overshadow long-term user value.
Over-fixation: While important, your NSM shouldn't be the only metric you care about. Balance it with other indicators of product and business health.
To overcome these challenges:
Regularly validate your NSM against user feedback and business outcomes
Foster a culture of questioning and continuous improvement
Use supporting metrics to provide context and catch unintended consequences
Key Takeaways
The North Star Metric is a single, guiding metric that encapsulates the core value your product provides to customers and aligns with your business goals.
Choosing the Right NSM is crucial. It should reflect customer value, be aligned with business success, and be easily measurable.
Implementation requires careful consideration, stakeholder involvement, and ongoing iteration to ensure it remains effective.
A good NSM drives growth and customer satisfaction, while a poorly chosen one can lead to misguided efforts.
Be aware of common pitfalls like choosing vanity metrics or over-fixating on a single number.
Regularly review and be prepared to adapt your NSM as your product and market evolve.
That’s a wrap for today!
How do you decide the NSM of your products? We’d love to hear from you!
Share in the comments below or reply to this email.
Until next time, keep innovating, keep iterating, and above all, keep being awesome.
Cheers!
Product Space






Good one